Hello my friends, today I will tell you about UTI - obstruction, ureter, bladder cancer, urinary tract and infection, urinary tract infection men and women
Obstructions
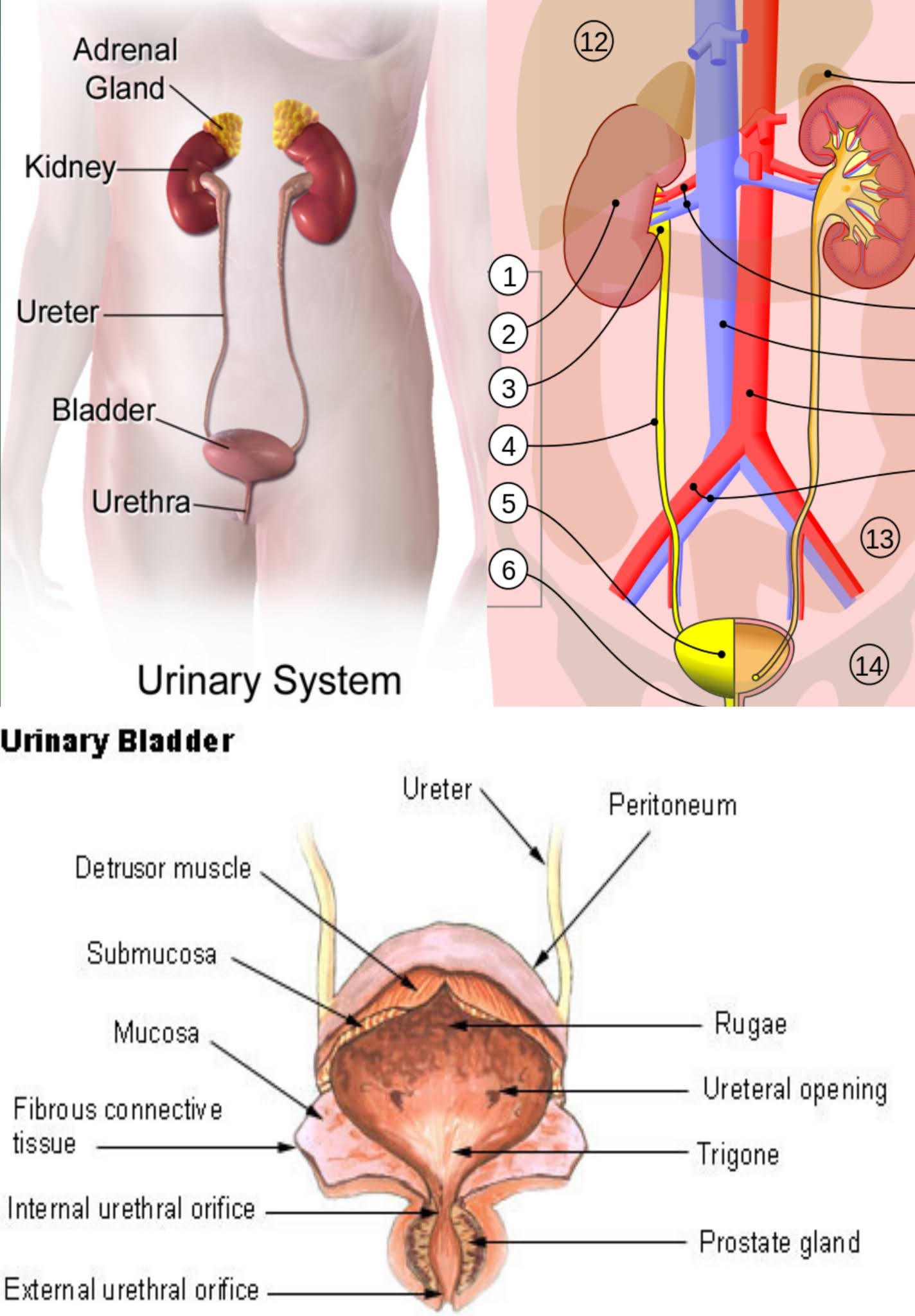
The most common abnormalities associated with urinary tract infections, and most important from the point of view of kidney damage, are blockages. The blockage may occur in the area where the renal urine merges with the collecting pelvic narrow ureter, or they may occur anywhere along the ureter. For example, a stone or congenital stricture can obstruct the ureter anywhere in its course. Or a tumor can cause blockage within the bladder that prevents both ureters from opening in the bladder, or it can result in congenital wounds, tumors, stones or hardening of the bladder neck.
 |
| urinary bladder |
Anywhere there is a barrier behind the urine, as the river goes behind a dam. Back pressure rises above the level of hydronephrosis, inflammation of the renal pelvis, and deformed and ureteric obstruction. Hydraulic pressure squeezes the renal tissue that begins to atrophy. Efficiency is gradually lost and the inflated kidneys are at risk of being completely damaged. When destruction of any nature is discovered, it must be removed by appropriate therapy to prevent irreparable damage.
Ureter
Injuries that tear, puncture, or otherwise obstruct a ureter allow urine to leak from the burst pipe into surrounding tissue like water. The repair is surgical. Hard and stone can cause obstruction. The tumor can cause bladder blockage and gross bleeding. The most important single difference between ureter and kidney lesions is that ureter blockage always produces pain, but renal lesions often do not. Pain warnings usually remove early diagnosis and obstruction that can cause further kidney damage.
bladder cancer
It is extremely important that individuals who have any difficulty or abnormality of urination should be carefully examined to find out if there is any lesion present in the bladder.
Bladder cancer is one of the most common in this country. It is almost as common as lung cancer, although it has not received as much publicity. At University Hospitals in Iowa City, more than 75 new patients with bladder cancer are seen annually.
The most common evidence of bladder cancer is largely bloody urine, but the frequency of urination and cloudy urine can also be important symptoms. When detected early, the outlook is good, when late, poor. Treatment includes removal of the tumor by a combination of surgical removal and radiation therapy. Small tumors can be removed through the urethra with a device called a rectoscope. Larger lesions require more radical sur
# urinary tract infection men
What are the symptoms of bladder infection in men?
- 1) Frequent urination.
- 2) Strong, persistent urges (urges)
- 3) during burning or tingling or just after 4) urination (dysuria)
- 5) Low grade fever.
- 6) Stinky urine with strong odor.
- 7) Blood in urine (hematuria)
How does a man get rid of urinary tract infection?
Physicians usually treat UTI with oral antibiotics. Your doctor will likely choose an antibiotic based on the likely source (such as your bladder) and the bacteria that usually causes your UTI. You will likely start taking those antibiotics before your urine test results are received.
How long does a UTI male last?
In general, most complex lower tract infections will be completely eradicated during five to seven days of treatment. Once you have finished taking antibiotics, your doctor may ask you to repeat the urine sample to confirm the bacteria has passed away.
# urinary tract infection women
What are the symptoms of UTI in women?
Symptoms of uti
- 1) Burning sensation while urinating.
- 2) Willingness to urinate continuously or intensely, even if you do.
- 3) Comes out a little.
- 4) Cloudy, dark, bloody or weird smelly urine.
- 5) Feeling tired or unstable.
- 6) Fever or chills (a sign that the infection may reach your kidneys)
- 7) Stomach or lower back pain or pressure.
Can urinary tract infection go away on its own?
What can happen if a UTI is untreated? If left untreated, some bladder infections will go away automatically. The main concern with delays in the treatment of UTIs is the discomfort they cause. Usually, UTI symptoms improve within a few days of starting antibiotics.
How long does a woman have a UTI?
With proper treatment, most incomplete urinary tract infections can be cured in two to three days. It may take several days for the symptoms of a kidney infection to go away completely.
How long does a UTI last?
Most UTIs can be fixed. Symptoms of a bladder infection often go away within 24 to 48 hours of treatment. If you have a kidney infection, it may take 1 week or more for symptoms to go away.
# Urinary tract and infection
What causes urinary tract infection?
Urinary tract infections are caused by microorganisms - usually bacteria - that enter the urethra and bladder, causing inflammation and infection. Although a UTI is most commonly in the urethra and bladder, bacteria can also travel to the ureter and infect their kidneys.
How do you know if you have a urinary tract infection?
Urinary tract infections do not always cause signs and symptoms, but when they do they may include:
- 1) A strong, persistent urge to urinate.
- 2) Burning sensation while urinating.
- 3) Frequent passing, small amounts of urine.
- 4) Urine that appears cloudy.
- 5) Urine that appears red, mauve or cola - a sign of blood in the urine.
What are the similar symptoms of UTI?
These include Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Trichomoniasis. Simple lab tests are available to distinguish UTI from STDs. Interstitial cystitis also has symptoms similar to urinary tract infections. It can occur in both men and women and may begin after UTI.







