Hello friend, today we will know that some special facts of meningitis __
 |
| meningitis |
A) What is the condition of meningitis?
B) What causes meningitis?
C) What are the symptoms of meningitis?
D) How is it diagnosed with meningitis?
E) How is meningitis Treatment?
Let's know...
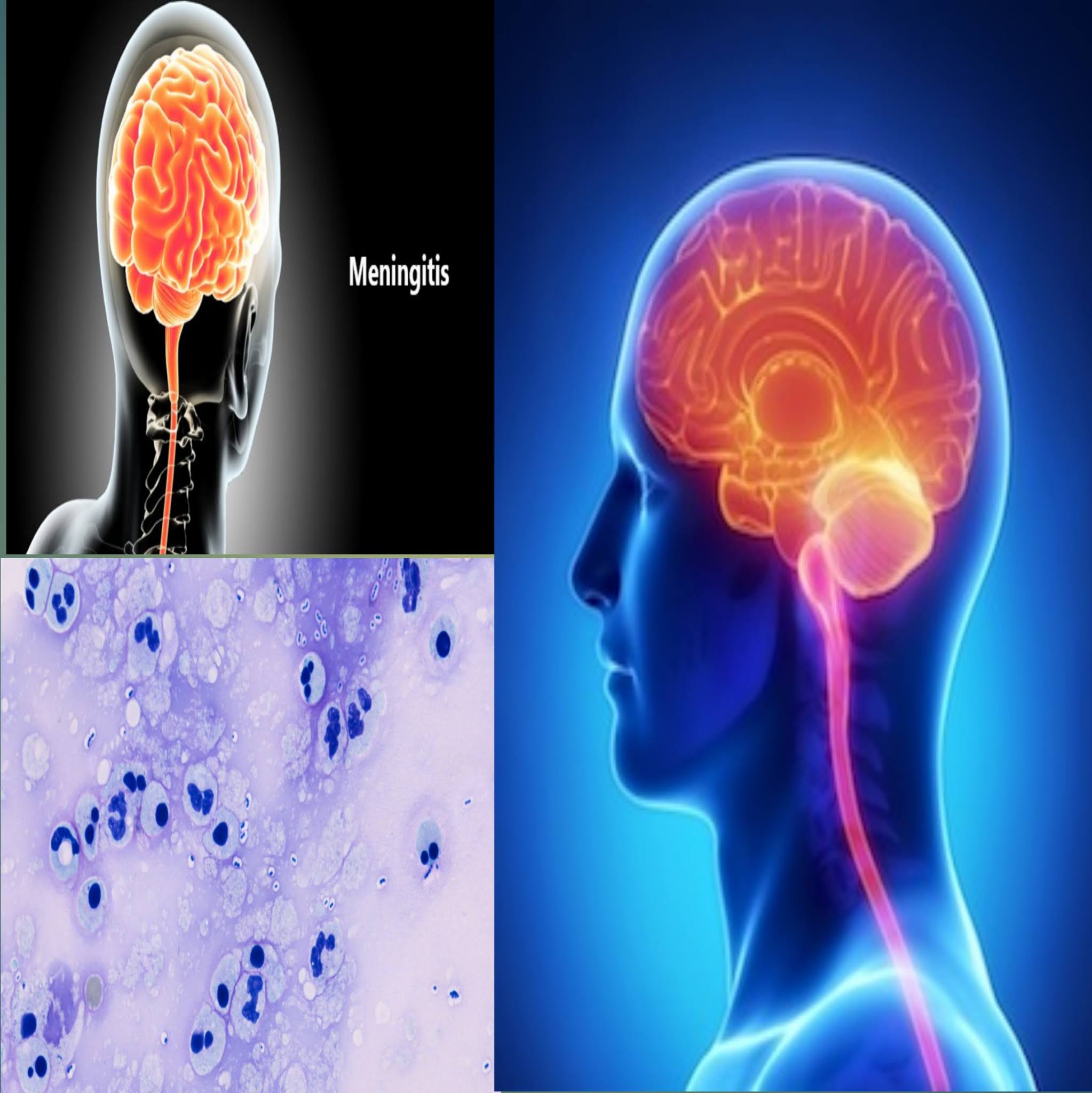
A) What is the condition of meningitis?
In this disorder, meninges become infected with the brain and spinal cord, usually as a result of bacterial infection Such inflammation may include all three meningeal membranes: dura mater, arachnoid and pia mater. Diagnosis is good and complications are rare, especially if the disease is diagnosed early and the infected organism reacts to antibiotics. However, untreated disease mortality is 70% to 100%. Pregnancy is bad for infants and the elderly.
 |
| condition of meningitis |
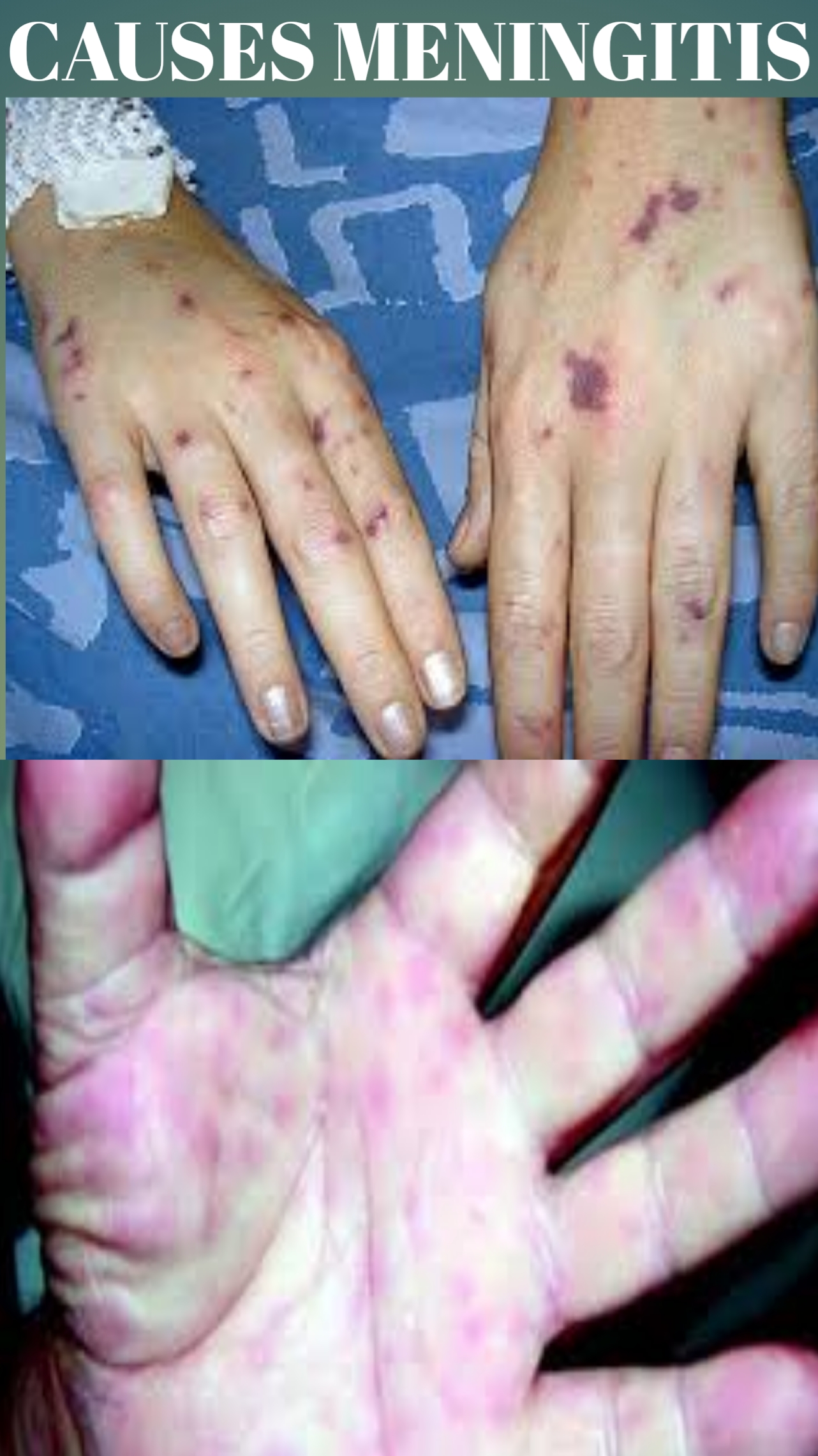
B) What causes meningitis?
Meningitis is almost always a complication of another bacterial infection: bacteria (especially pneumonia, pus in the body cavity, osteomyelitis or endocarditis), sinus or middle ear infection, encephalitis, myelitis or brain abscess.
This disorder may also follow a skull fracture, a penetrating head wound, lumbar puncture or ventricular shunt insertion. Aseptic inflammation of the brain and spinal cord membranes can also occur from a virus or other organism. Occasionally, no organism can be found. Inflammation of the brain and spinal cord membranes can promote congestion of adjacent tissues and destroy some nerve cells.
 |
causes meningitisC) What are the symptoms of meningitis? |
The cardinal symptoms of this disorder are similar to infection (fever, chills, malaise) and increased intracranial pressure (headache, vomiting and, rarely, inflammation of the optic disc). Signs of meningeal irritation include stiffness on the neck impotence, involuntary knee stiffness when the neck is flexed flexibly, when seated, exaggerated and symmetrical reflective, and inability to lift the legs and back so that the body and There is backache. The heel should be on the head and back.
Other symptoms are irregular heartbeat, irritability, excessive sensitivity to light, double vision and other visual problems and delirium, deep stupor and coma.
An infant may show signs of infection and is often quarrelsome and refuses to eat. Such a child may vomit a great deal, leading to dehydration.
As the disease progresses, torsion, seizures (in 30% of infants), or coma may develop. Most older children have the same symptoms as adults. In the sub-form, the onset may be gradual.
 |
| symptoms of meningitis |
D) How is it diagnosed with meningitis?
A lumbar puncture (spinal tap), showing typical cerebrospinal fluid findings, and some physical examination findings usually establish this diagnosis. Fluid may appear cloudy or milky white, depending on the number of white blood cells present. Protein levels in cerebrospinal fluid are high; Sugar levels may decrease. (In subacute disease, fluid extracts can vary.) Cerebrospinal fluid culture and susceptibility tests usually identify an infected organism unless it is a virus.
To help determine the major sites of infection, the doctor will take cultures of blood, urine and nasal and throat secretions; chest X-ray; And an electrocardiogram. Abnormally high levels of white blood cells and electrolyte abnormalities are also common. Computed tomography (commonly referred to as a CAT scan) can control brain hematoma, bleeding, or tumors.
 |
| diagnosed with meningitis |
E) How is meningitis Treatment?
To treat this disorder, the person receives appropriate antibiotic therapy and vigorous supportive care. Typically, intravenous antibiotics are given for at least 2 weeks, followed by oral antibiotics. Such antibiotics include bicillin, omnipen or nafcil. However, if the person is allergic to penicillin, chloromycetin or controx may be given. Other drugs include cardiac glycosides such as lanoxine to control the heartbeat, osmitrol to reduce brain inflammation, an anti-seizure medication to reduce headaches (usually intravenous) or to reduce discomfort. Is included for. This includes sedative or aspirin or tylenol (or another acetaminophen product) fever.
Supportive measures include bed rest, reduction in body temperature and measures to prevent dehydration. If nasal cultures are positive for some cultures, then the individual should be isolated. Of course, treatment includes appropriate therapy for any co-condition such as pneumonia.






