What is this condition?
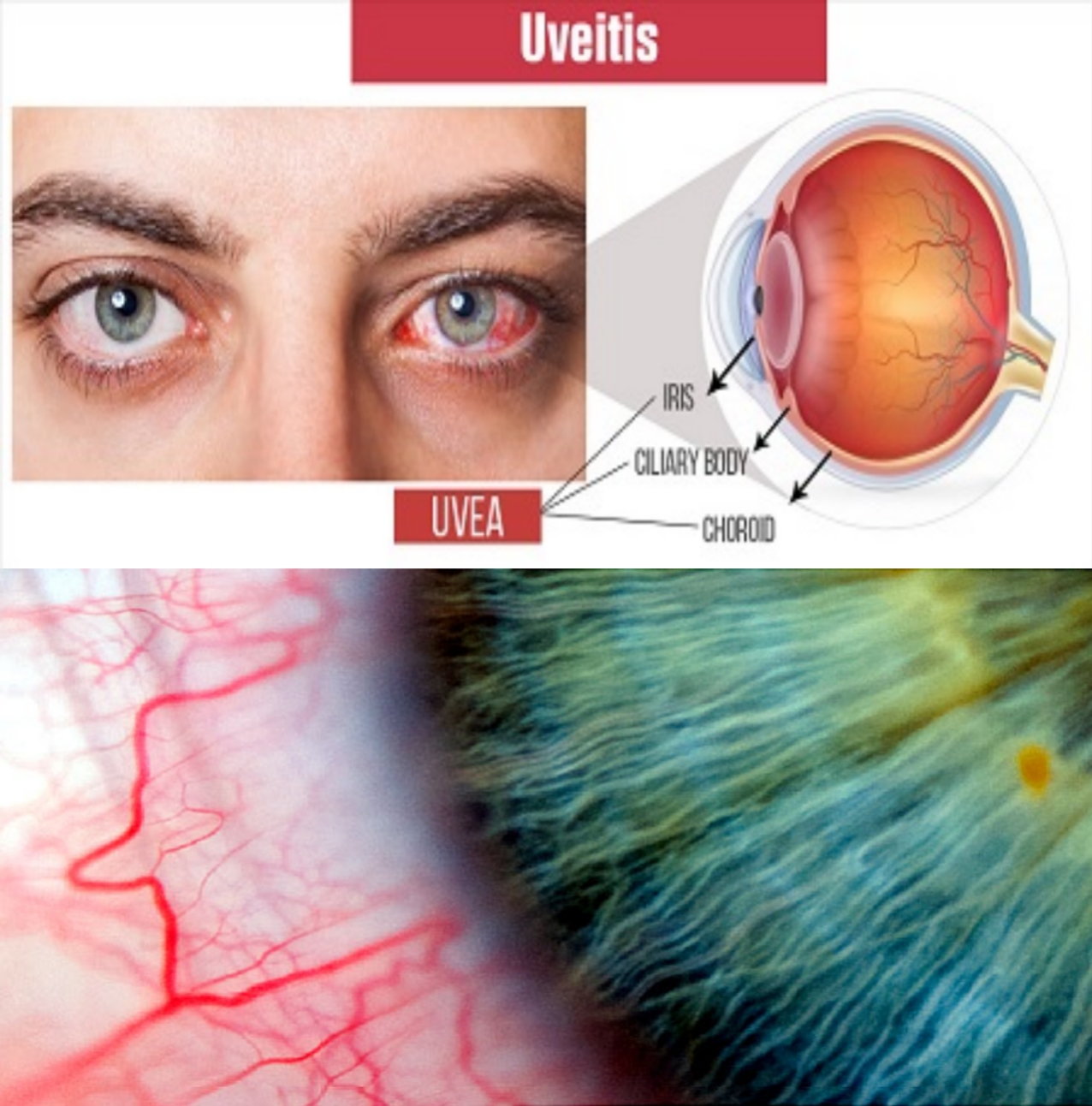
Uveitis is inflammation of the urethra of the eye. (The uveal tract includes the iris, choroid, and associated tissue structures.) The disorder occurs in the form of anterior uveitis, which affects the iris (iritis) or both the iris and the ciliary body (iridyclitis); In the form of posterior uveitis, which either affects the choroid (choroiditis) or affects both the choroid and retina (choriorenitis); Or as panuveitis, which affects the entire urinary tract.
Untreated anterior uveitis leads to posterior uveitis, causing scarring, cataracts, and glaucoma. With immediate treatment, anterior uveitis usually subsides after a few days to several weeks; However, there is a possibility of recurrence. Postoperative uveitis usually causes some residual vision loss and markedly blurred vision.
what causes it?
In most cases, the cause of uveitis is unknown. But it can occur as a result of allergies, bacteria, viruses, fungi, chemicals, traumatic injuries, surgery, or systemic diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and toxoplasmosis.
What are the symptoms?
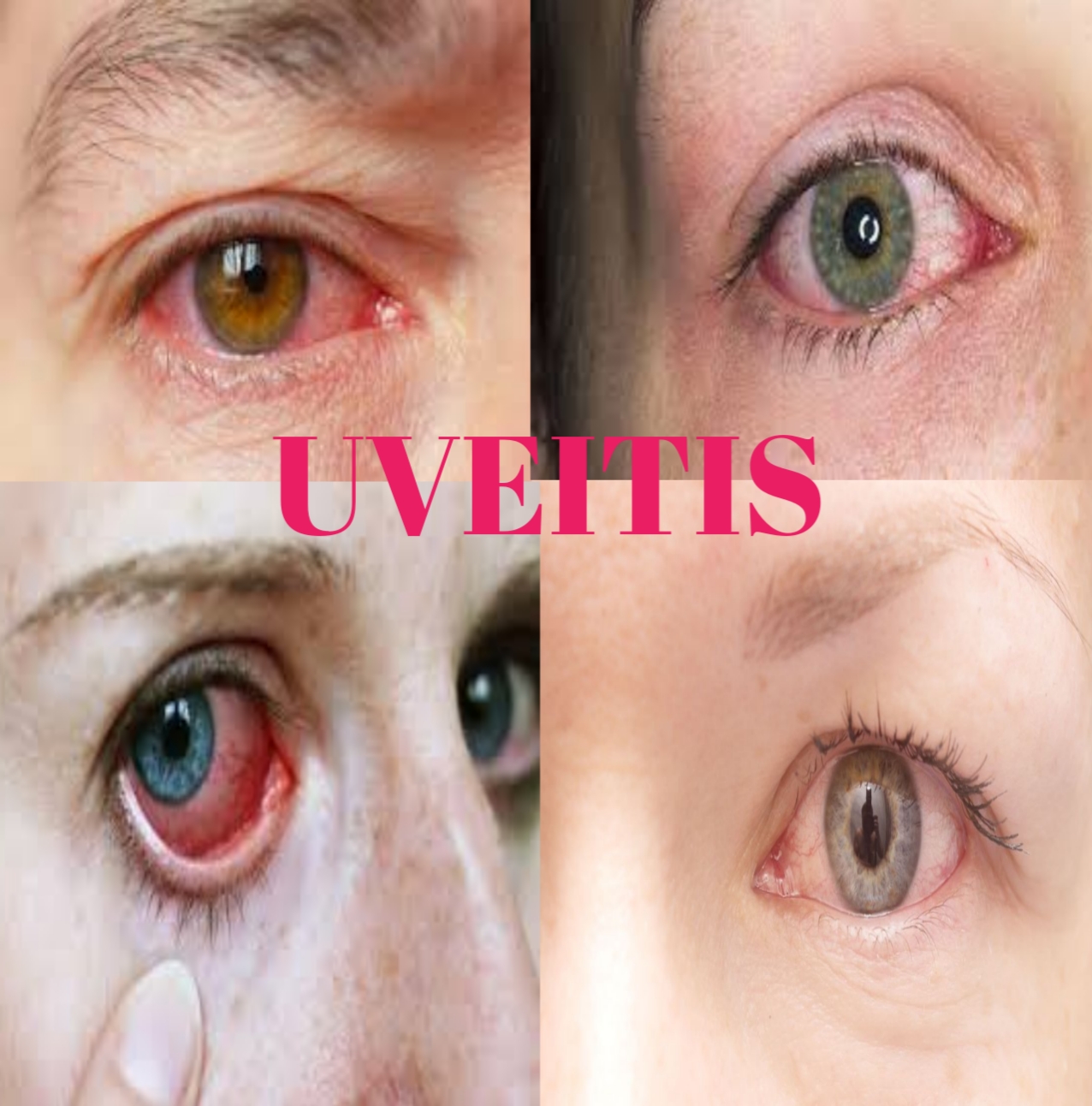
Anterior uveitis produces moderate to severe pain in one eye; Severe ciliary congestion; Sensitivity to light; Tearing; A small, non-dormant pupil; And blurred vision. Postoperative uveitis begins with acutely reduced or complained of blurred vision or floating spots. There may also be sensitivity to pain and light.
How is it diagnosed?
In anterior and posterior uveitis, a slit-lamp examination shows a "flare and sail" pattern, which appears to pass light with smoke. It also reflects the increasing number of cells in the inflamed area. With a special lens, doctors can also use slit-lamps and eye exams to identify active inflammatory fundus lesions associated with the retina or choroid.
After hysterectomy, serological tests can determine whether toxoplasmosis is the cause.
How is Treatment?
Uveitis requires vigorous and prompt management, including any known underlying cause and application of idrops or ointment, such as 1% atropisol or steroids. For severe uveitis, the therapy includes oral steroids. However, prolonged steroid therapy may increase the risk of intraocular pressure and cataract.